Purpose
-
- Guiding Korean language learning and promoting Korean worldwide for non-native speakers and overseas Koreans.
- Assessing and certifying Korean proficiency for university admission, employment, and official use.
Eligibility
-
- Open to all foreigners and overseas Koreans whose native language is not Korean.
Main Applications
-
- Admission to and graduation from Korean universities and graduate schools for foreigners and overseas Koreans
- Enrollment and academic management for government-invited foreign scholarship programs
- Fulfillment of credit and graduation requirements in Korean language-related departments at overseas universities
- Employment at domestic and international companies and public institutions
- Acquisition of residency or work visas (including permanent residency)
Test Fields
-
- TOPIK I (Beginner), TOPIK II (Intermediate & Advanced), and TOPIK Speaking
- Paper-Based Test (PBT) and Internet-Based Test (IBT, currently in pilot operation)
- Test Areas: Listening, Reading, Writing (only for TOPIK II), and Speaking (separate test)
Number of Questions & Test Duration
Category |
TOPIK PBT |
TOPIK IBT |
TOPIK Speaking |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TOPIK I (Beginner) |
TOPIK II (Intermediate) |
TOPIK I (Beginner) |
TOPIK II (Intermediate) |
||
|
Number of questions |
30 / 40 |
50 / 50 / 4 |
26 / 26 |
30 / 30 / 3 |
6 |
|
Number of Questions |
100Min |
180Min |
70Min |
125Min |
30Min |
Score by Grade
Section |
Grade |
TOPIK PBT |
TOPIK IBT |
|---|---|---|---|
TOPIK I (Beginner) |
Grade 1 |
80 ~ 139 |
121 ~ 235 |
Grade 2 |
140 ~ 200 |
236 ~ 400 |
|
TOPIK II (Intermediate) |
Grade 3 |
120 ~ 149 |
191 ~ 290 |
Grade 4 |
150 ~ 189 |
291 ~ 360 |
|
Grade 5 |
190 ~ 229 |
361 ~ 430 |
|
Grade 6 |
230 ~ 300 |
431 ~ 600 |
Section |
Grade |
Score |
|---|---|---|
TOPIK Speaking |
Grade 1 |
20 ~ 49 |
Grade 2 |
50 ~ 89 |
|
Grade 3 |
90 ~ 109 |
|
Grade 4 |
110 ~ 129 |
|
Grade 5 |
130 ~ 159 |
|
Grade 6 |
160 ~ 200 |
TOPIKExam schedule and application website URL : https://www.topik.go.kr
Purpose
-
- To assess the Korean language proficiency and understanding of Korean society among foreign job seekers
- To use the results as an objective selection criterion when compiling the list of foreign job seekers
- To encourage the entry of individuals with a basic understanding of Korea and to promote better adaptation to life in Korea
Eligibility
-
- Individuals aged between 18 and 39 years old
- Citizens from a Sending Country that participates in the Employment Permit System (EPS)
* Sending Country : A country that has signed an agreement with the Korean government under the Employment Permit System (EPS) to legally dispatch foreign workers to Korea.
Main Applications
-
- Eligibility requirements for non-professional employment in Korea
- Conditions for participation in the Employment Permit System (EPS)
- Procedures for obtaining E-9/E-10 visas
- Job seeker registration for workers from a Sending Country
Test Fields
-
- EPS-TOPIK covers a single field.
- It is administered as a Paper-Based Test (PBT) and a Computer Based Test (CBT), with the CBT format varying by country.
- Test sections include Listening and Reading.
Number of Questions & Test Duration
Category |
EPS - TOPIK |
|---|---|
|
Number of questions |
20 / 20 |
|
Exam time |
50Min |
Score by Grade
- Evaluation Method: Relative Evaluation
- Selection Criteria: Candidates who score above the minimum passing score for each industry category are selected based on ranking until the planned number of recruits is reached.
- 1. Manufacturing and Shipbuilding Industries: 55 points or higher out of 100
- 2. Other Industries: 45 points or higher out of 100
- 3. Special Fisheries Program: 27 points or higher out of 90 (Pass/Fail)
* EPS-TOPIK Exam schedule and application website URL : https://epstopik.hrdkorea.or.kr
Purpose
-
- Assessing the Korean language proficiency of foreigners and overseas Koreans.
- Designed to promote the Korean language among non-native speakers, this test provides learning guidance to help overseas Koreans and foreigners rapidly maximize their Korean language skills for practical use.
Eligibility
-
- Korean language learners who wish to assess their proficiency
- Students seeking admission to universities in Korea
- Individuals aiming to gain employment at Korean companies
- Foreigners, immigrants, and members of multicultural families
Main Applications
-
- Evaluation of standard language usage and proper sentence construction skills by broadcasting companies and media organizations
- Used as supporting documents or self-introduction materials when applying for jobs
- Utilized for Korean language education completion assessments or diagnostic purposes
- Recognized as proof of Korean language proficiency or supplementary material for graduation requirements for international students
Test Fields
-
- There are two types of tests: KBSKLT-I and KBSKLT-II
- The tests are administered as Paper-Based Test (PBT), Internet-Based Test (IBT), and Computer-Based Test (CBT).
Number of Questions & Test Duration
Category |
KBSKLT |
|
|---|---|---|
KBSKLT – I |
KBSKLT – II |
|
|
Number of questions |
|
|
|
|
90Min |
140Min |
Score by Grade
Grade |
KBSKLT – I |
KBSKLT – II |
|---|---|---|
Grade 1 |
30 ~ 74 |
30 ~ 74 |
Grade 2 |
75 ~ 119 |
75 ~ 119 |
Grade 3 |
120 ~ 164 |
120 ~ 164 |
Grade 4 |
165 ~ 200 |
165 ~ 209 |
Grade 5 |
- |
210 ~ 254 |
Grade 6 |
- |
255 ~ 300 |
KBSKLT Exam schedule and application website URL : https://www.kbsklt.com
Purpose
-
- Providing guidance for Korean language learning and promoting the global spread of Korean
- Comprehensive assessment of Korean language proficiency with a focus on communication skills
- Supporting practical applications both domestically and internationally (e.g., study abroad, employment)
Eligibility
-
- Open to all foreigners and overseas Koreans whose native language is not Korean.
Main Applications
-
- Utilized for the selection and admission of outstanding foreign talent
- Used as proof of Korean language proficiency for studying in Korea
- Referenced during visa applications and residency qualification reviews
Test Fields
-
- SKA covers a single field.
- The test is administered as a Paper-Based Test (PBT) and a Computer-Based Test (CBT).
- Test sections include Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking.
Number of Questions & Test Duration
Category |
SKA |
|
|---|---|---|
Number of Questions |
Listening/Reading/Writing |
20 / 20 / 2 |
Speaking |
2 |
|
Test Duration |
140Min |
|
Score by Grade
Grade |
SKA |
|
|---|---|---|
Beginner Learne |
Grade 1 |
108 ~ 215 |
Grade 2 |
216 ~ 295 |
|
Intermediate Learner |
Grade 3 |
296 ~ 400 |
Grade 4 |
401 ~ 495 |
|
Advanced Learner |
Grade 5 |
496 ~ 580 |
Grade 6 |
581 ~ 800 |
|
SKA Exam schedule and application website URL : https://ska.ksif.or.kr
Purpose
-
- Assessment of Korean language proficiency for foreigners and overseas Koreans
- Providing guidance for Korean language learning and verifying learning achievement
- Utilized for studying abroad in Korea, employment, visa applications, and residency qualification reviews
- Fulfilling credit and graduation requirements for Korean language-related departments at overseas universities
Eligibility
-
- Foreigners and overseas Koreans whose native language is not Korean
- Individuals seeking admission to Korean universities or graduate schools
- Individuals aiming to work at Korean companies or Korea-related enterprises
- Anyone wishing to have their Korean language proficiency evaluated
Main Applications
-
- Used for document screening during admission to Korean universities (freshman or transfer) and employment at Korean companies
- Preferred qualification or additional points given when selecting and promoting foreign employees
- Applied as a selection criterion and evaluation tool for midterm and final exams for international students
- Utilized as a selection criterion for foreign trainees and overseas Koreans
Test Fields
-
- There are four types of tests: B-KLAT (Basic), KLAT (Beginner), KLAT (Intermediate), and KLAT (Advanced).
- The tests are administered as Paper-Based Tests (PBT) and Internet-Based Tests (IBT).
- Test sections include Listening, Reading, Writing, Vocabulary, and Grammar.
Number of Questions & Test Duration
Category |
B-KLAT(Basic) |
KLAT(Beginner) |
KLAT(Intermediate) |
KLAT(Advanced) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Number of Questions |
Listening |
Reading |
Listening |
Vocabulary and Grammar |
Reading |
Listening |
Vocabulary and Grammar |
Reading |
Listening |
Reading |
Writing |
25 |
25 |
30 |
25 |
20 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
3 |
|
Test Duration |
80Min |
110Min |
120Min |
165Min |
|||||||
Score by Grade
Grade |
SKA |
Recommended Study Hours |
|
|---|---|---|---|
B-KLAT(Basic) |
Grade 1 |
92 ~ 139 |
150 to 200 hours |
Grade 2 |
140 ~ 200 |
||
KLAT(Beginner) |
Grade 1 |
80 ~ 139 |
Up to 400 hours |
Grade 2 |
140 ~ 495 |
||
KLAT(Intermediate) |
Grade 3 |
80 ~ 139 |
401 to 800 hours |
Grade 4 |
140 ~ 200 |
||
KLAT(Advanced) |
Grade 5 |
150 ~ 239 |
801 hours or more |
Grade 6 |
240 ~ 300 |
||
※ To pass KLAT Level 1, candidates must achieve the minimum required scores in each section
(Listening: 27 points, Vocabulary/Grammar: 14 points, Reading: 18 points)
※ If the B-KLAT (Basic) test result falls below Level 1, it will be classified as 'B-KLAT No Grade.'
KLAT Exam schedule and application website URL : http://www.kets.or.kr
Reliability Analysis of the PLAYTOPIK Question Generation System
PLAYTOPIK Question System Governance
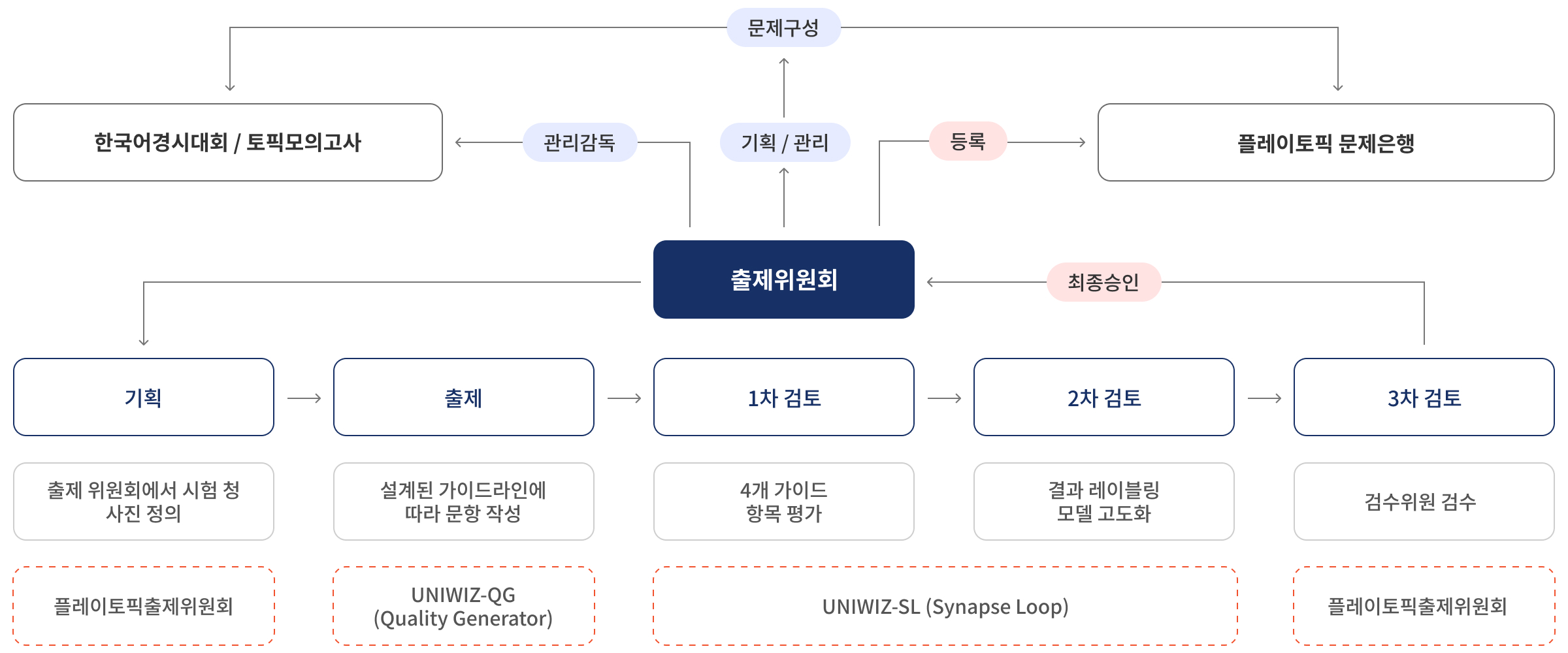
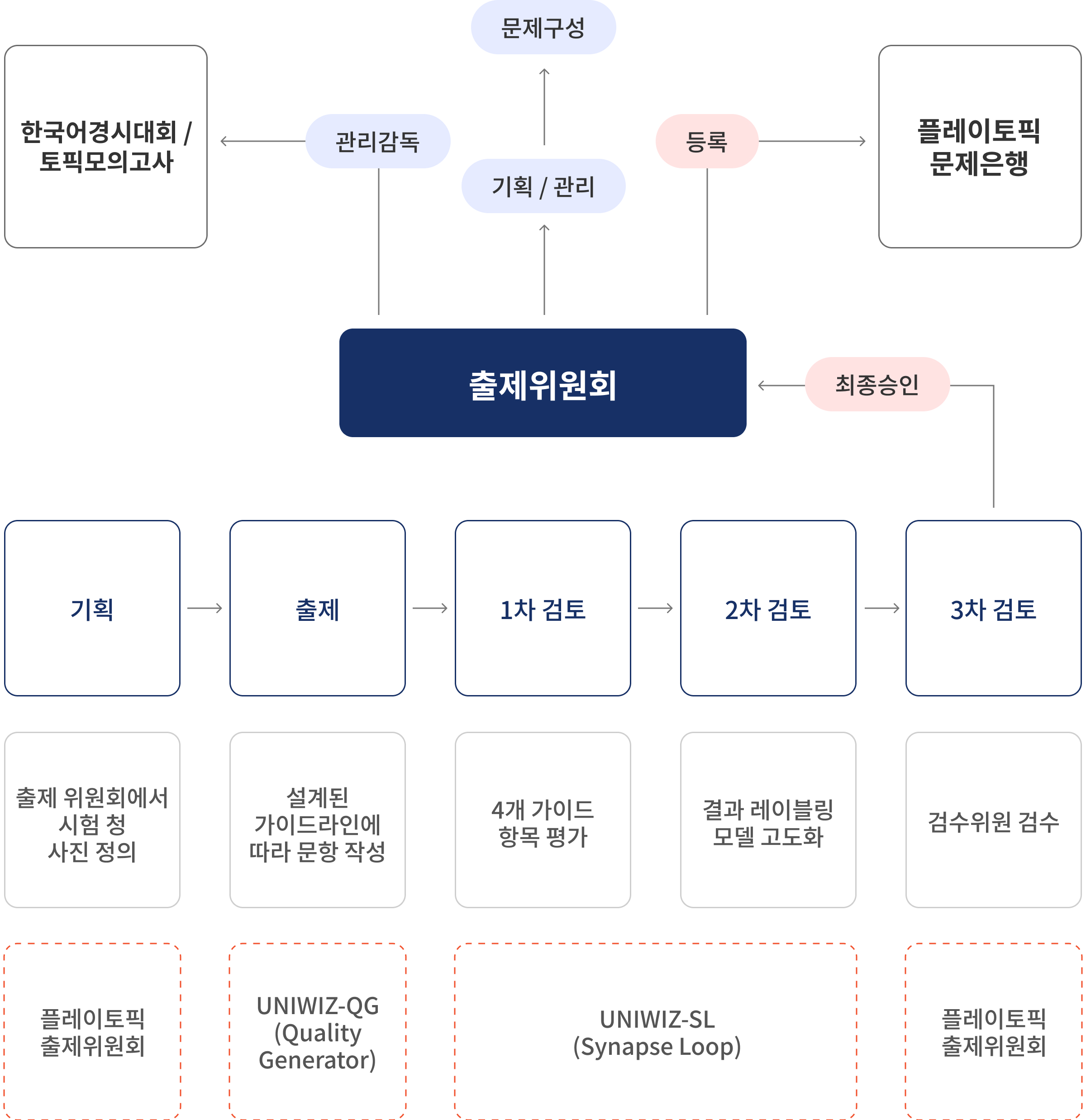
Four Core Elements of Question Creation
-
Systematic Design
- A multi-layered and sophisticated difficulty control system is established across four dimensions: vocabulary, grammar, text, and culture.
-
Cultural Expertise
- Understanding the high-context characteristics of Korean culture, systematizing them by level, and reflecting them in assessment.
- Adjusting the depth of cultural understanding to include uniquely Korean emotional concepts such as “nunchi,” “jeong,” “che-myeon,” and “han.”
-
Quality Assurance
- Ensuring validity and reliability of all questions through a 3-step verification system and four quality control standards.
- Final quality assurance through review by evaluators (human + AI) and final validation by the question committee.
-
Relevance to the Times
- While maintaining traditional assessment principles, modern materials reflecting learners’ real-life digital language environments are actively utilized.
- Incorporating modern contexts such as messenger conversations, online shopping, and K-POP into the questions.
Beyond simply generating questions, PLAYTOPIK analyzes past TOPIK test questions to
structure and systematize test creation and evaluation criteria, providing a consistent and fair Korean proficiency assessment platform.
Systematic and Professional Framework for Question Creation and Evaluation
-
Clear Difficulty-Level Classification System
PLAYTOPIK’s Strength : Multi-layered difficulty control across four dimensions
- Vocabulary, grammar, text, and culture
- More than three detailed levels within each dimension
- Precise difficulty settings with a 10-level sentence structure classification
Vocabulary
Over three levels of vocabulary difficulty classification
Grammar
Over three levels based on syntactic complexity
Text
Classification based on sentence length and complexity
Culture
Three levels: Universal → Korean Context 1 → Korean Context 2
-
Evaluation of Practical Language Proficiency
PLAYTOPIK’s Approach
- Reflecting diverse real-life situations, from daily topics to modern digital media
- Actively utilizing modern materials such as messenger chats, online shopping, and K-POP
- Assessing comprehension of practical texts such as charts, notices, and advertisements
Emphasis on Practicality
Real Conversations Messenger chats, SNS posts, etc.
Modern Services Online shopping, banking services, etc.
Public Information Notices, instructions, signs, etc.
Advertising & Promotion Charts, ads, promotions, etc.
Sophisticated Understanding of Cultural Contexts
-
Systematic Classification of Korean Contexts
PLAYTOPIK’s Distinctive Approach
- Three-tier structure: Universal Situations → Korean Context 1 (TOPIK I) → Korean Context 2 (TOPIK II, Levels 5–6)
- Assessing indirect communication reflecting the characteristics of high-context culture
- Including unique emotional concepts of Korean culture such as “nunchi,” “jeong,” “che-myeon,” and “han.”
Universal Situations
Friends, visits, invitations
Korean Context 1 (TOPIK I)
First birthday parties, kimchi festivals, K-POP
Korean Context 2 (TOPIK II, Levels 5–6)
Generational values, the dilemma of “jeong”
-
PLAYTOPIK’s Design
- TOPIK I: Balanced between traditional culture (first birthday parties, kimchi festivals) and modern culture (K-POP classes)
- TOPIK II Advanced: Complex social issues such as generational value conflicts and dilemmas between “jeong” and public responsibility
- Reflecting high-context characteristics of Korean culture through cultural context
Interpersonal Relations (friends, visits)
Cultural Expression (traditional, modern)
Cultural Dilemmas (jeong, responsibility)
Indirect Communication
Comprehensive Evaluation Domains and Quality Management System
-
Diverse Question Types
Core Assessment Elements of PLAYTOPIK
- Measuring “main idea grasping,” “detail comprehension,” and “inference” from multiple perspectives
Topic Identification Type
Understanding the main idea
Fill-in-the-Blank Type
Integrated vocabulary and grammar
Chart/Notice Type
Information processing
Short Passage Consistency Type
Fact checking
Main Idea Identification Type
Understanding implied meaning
Long Passage Comprehension Type
Integrated understanding
Sentence Ordering Type
Discourse structure
Sentence Insertion Type
Information flow
Connector Selection Type
Logical relationship
Purpose Identification Type
Pragmatics
Long Passage Inference Type
Contextual inference
-
Multi-layered Quality Verification
PLAYTOPIK’s Verification Process
- 3-step verification system and four quality control standards
Step 1: AI + Human Question Creation
Collaboration between AI and experts to secure diverse question sets
Step 2: Review by Evaluators
Validation of content validity, linguistic naturalness, and cultural appropriateness by experts and AI
Step 3: Final Validation
Final quality assurance and direction setting by the question committee
Vocabulary
Building and adhering to a vocabulary database by curriculum level
Grammar
Utilizing practical grammar elements centered on communicative functions
Text
Providing realistic questions through natural and authentic discourse composition
Culture
Assessing cultural understanding by harmoniously reflecting universal situations and Korean contexts